Types of inflammation 《Acute and chronic inflammation》
“Inflammation” is a defensive reaction that tries to remove and repair harmful things when a body receives the damage. Inflammation can be caused by physical factors such as injury (spraining, bruising, etc.), and biologically caused by pathogenic bacteria such as when catching a cold.
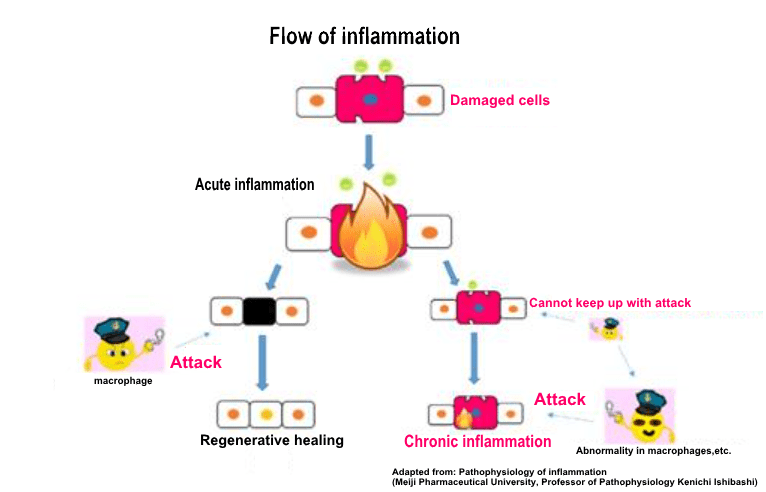
Inflammation is generally categorized over course of time. Acute inflammation is defined as symptoms that resolve within a short period of time, and chronic inflammation is defined as inflammation that is prolonged. As the main signs of inflammation is redness, heat sensation, swelling, pain, etc., but with these symptoms, inflammation goes to calming down.
 However, sometimes the response cannot be caught up, and if a small amount of damage is repeatedly received, a small inflammatory reaction may persist and shift to a chronic inflammatory state, which is called “chronic inflammation”. Chronic inflammation is called a “silent killer” because it is difficult to see the symptoms and gradually affects the surrounding cells and tissues gradually from the inflamed area. Allergic diseases such as asthma and atopic dermatitis are also classified as chronic inflammation because they persist for a long time. More recently, it has become clear that chronic inflammation is greatly involved in the development of lifestyle-related diseases and Alzheimer’s disease.
However, sometimes the response cannot be caught up, and if a small amount of damage is repeatedly received, a small inflammatory reaction may persist and shift to a chronic inflammatory state, which is called “chronic inflammation”. Chronic inflammation is called a “silent killer” because it is difficult to see the symptoms and gradually affects the surrounding cells and tissues gradually from the inflamed area. Allergic diseases such as asthma and atopic dermatitis are also classified as chronic inflammation because they persist for a long time. More recently, it has become clear that chronic inflammation is greatly involved in the development of lifestyle-related diseases and Alzheimer’s disease.
Here, is introduction of research on the action of Asaigermanium on “rheumatoid arthritis” which is classified as chronic inflammation (autoimmune disease) conducted by Asai Germanium Research Institute.
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is caused by an abnormality in the system called “immunity” that protects the body from external enemies such as bacteria and viruses.
In joints with rheumatoid arthritis, the synovial membrane grows and it responds to immunity and starts to attack the joints, causing swelling and pain. This prevents the joints from normal functioning.
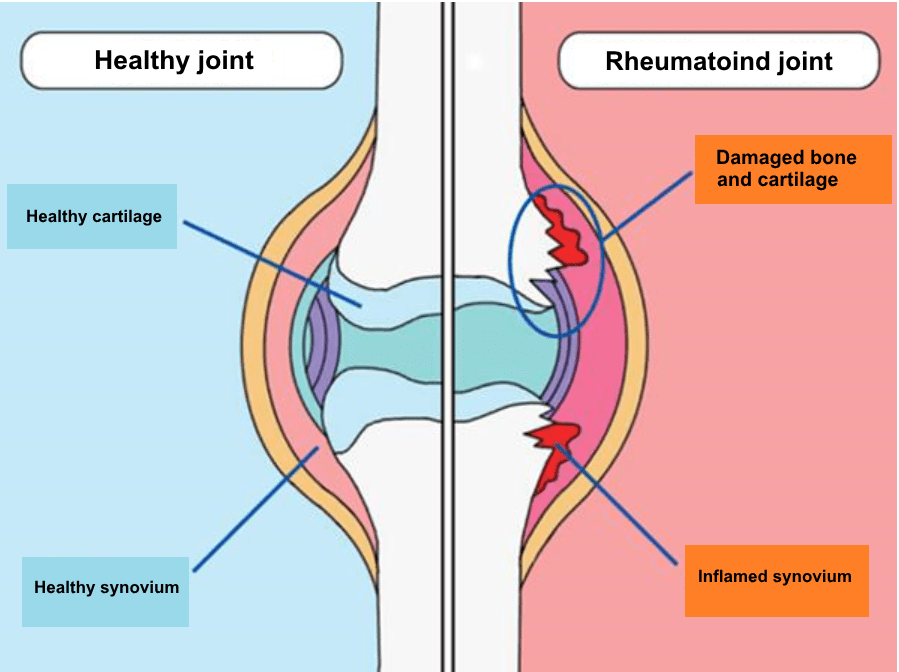
Recently, it has been found that rheumatoid arthritis is caused by the production of a protein responsible for information transmission between immune cells called cytokines * . If it is produced in large quantities over a long period of time, the inflammation will last longer, and if the symptoms worsen, it will affect the ligaments and bones and gradually deform accompanied by pain.
* Among cytokines related to inflammation and immunity, IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α are known as pro-inflammatory substances (substances that promote inflammation). In particular, IL-6 and TNF-α both activate osteoclasts that break bone. The longer the pro-inflammatory substance is produced, the greater the pain and deformation, as osteoclasts continue to be active.
Experiments using rheumatoid arthritis model
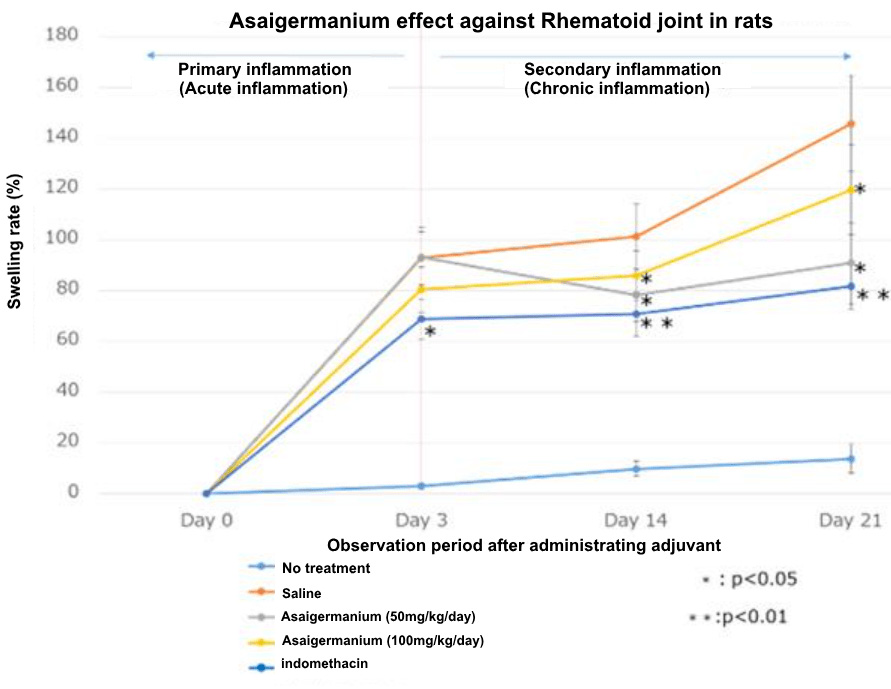
Experiment ① Experiment using rat adjuvant arthritis model
Adjuvant * arthritis model is a pathological model that reflects to human rheumatoid arthritis.
Test
Adjuvant was injected into the posterior area of the left leg of 6 rats per group, and the degree of swelling (swelling rate) after 3, 14, and 21 days was compared in the following 5 groups.
(1) Untreated group
(2) Oral administration of physiological saline
(3) A group of oral administration of 50 mg/kg body weight of Asaigermanium per day
(4) A group in which 100 mg/kg body weight of Asaigermanium was orally administered per day
(5) Group administered 0.1 mg/kg body weight of indomethacin, an anti-inflammatory agent, per day.
Result-1
Compared to the group administered with saline, the group administered with Asaigermanium showed significant effects not only for acute inflammation but also on chronic inflammation (chronic arthritis) 14 and 21 days after injection of adjuvant.
Result-2
The bones of the limbs on the 25th day after the adjuvant injection were observed with soft X-ray photographs, and the bone destruction of the groups administered with physiological saline seemed to be progressing. In the Asaigermanium administration group, bone lesions are also suppressed, and the state is similar to the control group.
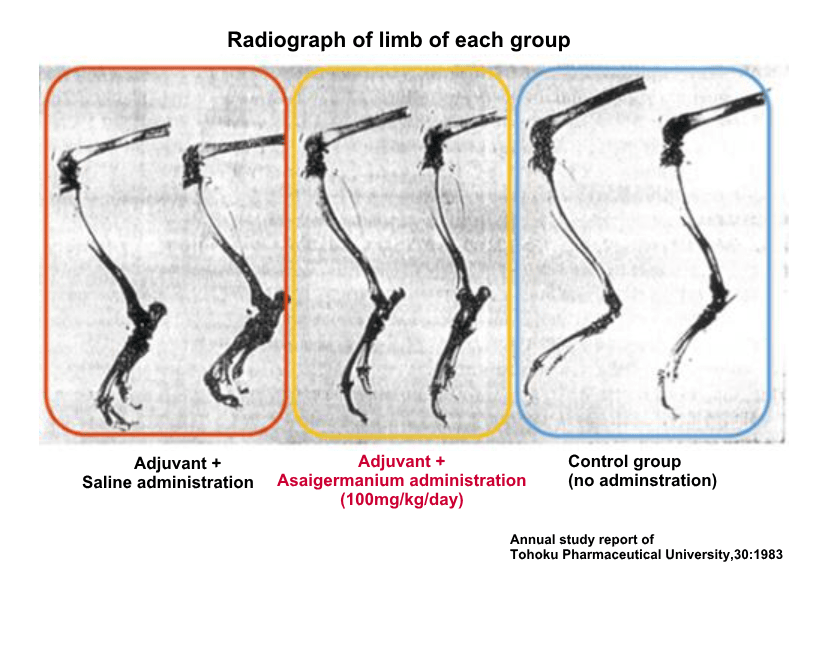
* Adjuvant: A non-specific immunostimulator (antigenic reinforcing agent) that has the effect of enhancing the immune response of cells.
Effects of Asaigermanium on rheumatoid arthritis
Experiment ② Clinical trial of Asaigermanium for rheumatoid arthritis
Test
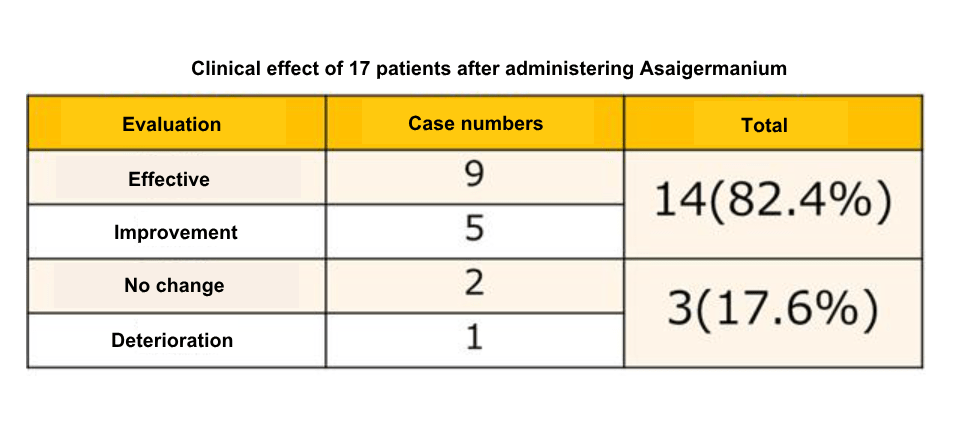
17 patients with rheumatoid arthritis took 1500 mg of Asaigermanium per day for 6 months, interview to patients as their doctors determined their condition.
Result-1
9 people were judged to be better (effective)than the same season 1-2 years ago, and 6 had improved number of painful joints, morning stiffness, and daily activity (improvement) , 82.4% of overall patients had some type of effect.
Result-2
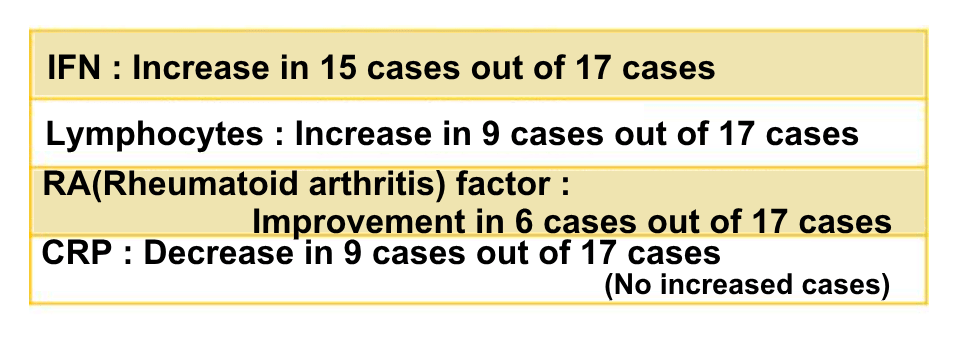
15 out of 17 patients who took Asaigermanium was seen with increased production of interferon (IFN) *1 . Interferon has an immunoregulatory function, but it has been shown that rheumatoid patients decrease the production. The other indicators *2 also have shown trend of improvement.
The latest research has reported that IFN enhanced with Asaigermanium has the effect of suppressing the production of pro-inflammatory substances such as TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6 that exacerbate the inflammatory response. In addition, IFN has the effect of suppressing osteoclasts that destroy bones. It is thought that this leads to suppression of pain and joint deformation.
*1 In the studies conducted so far, the interferon induced by Asaigermanium is γ-type, and the interferon in which the production ability is induced is assumed to be γ-type.
*2 CRP: A protein called C-reactive protein that elevates in the blood when inflammation occurs in the body. If inflammation is occurring, this number will increase.
Inflammation and Asaigermanium
It was found that administration of Asaigermanium to a rheumatoid arthritis model in rats significantly suppresses swelling, and also suppresses bone lesions. In human trials, more than 80% of patients were determined to have improved symptoms by taking Asaigermanium. In addition, production of interferon that adjusts the immune system was also observed, which proved to have a certain effect on rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition to the chronic inflammation introduced here, it has been reported that the effect of Asaigermanium on inflammation is also effective in tests using acute and subacute inflammation models in mice and rats.
References
1.Shigeru Arimori, Miyoko Furuta 1982 “Effect of Ge-132 on Chronic rheumatoid arthritis”, Medicine and Biology 104 (4): 211-213 (in Japanese)
2.Murakami Masaaki, Arima Yasunobu, Uemura Daisuke 2012 “Activation of IL-6 amplifier and entry of immune cells into the central nervous system organs” “Infection, inflammation and immunity” 42 (3): 28-40 (in Japanese)
3.T cells that induce osteoclasts 2008 “T cells that induce osteoclasts” “Renal and bone metabolism” 21 (1): Page unknown (in Japanese)
4.Shigeru Arimori, Laszio Pronai 1991 “Effect of Ge-132 on superoxide scavenging activity of immune diseases” “BIOTHERAPY” 5 (4): 708-712 (in Japanese)
5.Kazuhiro Yokota 2013 “Functional analysis of osteoclast-like cells induced by TNF / IL-6 in rheumatoid arthritis” Saitama Medical University Journal 40 (1): 28-31 (in Japanese)
6.Aoi Akitsu, Yoichiro Iwakura 2011 “Functions of IL-17 Family” “Rheumatology” 47 (1): 101-110 (in Japanese)
7.Naoko Nishimura “Cancers and Chronic Inflammation That I Have Found So far” www.natureasia.com/en-us/nature/ad-focus/detail/100909/1 (in Japanese)
8.Kenichi Sasaki, Masaaki Ishikawa, Giichi Takayanagi ,Keiko Monma 1983 “Effects of the immunomodulator organic germanium compound Ge-132 on adjuvant arthritis in rats” Tohoku Pharmaceutical University Annual Report 30: 143-147 (in Japanese)
9.Shinobu Furusawa, Tsutomu Fujimura, Iwao Hashimoto, Yumi Kitagawa, Kenichi Sasaki, Giichi Takayanagi 1987 “Effect of 2-Carboxyethylgermanium Sesquioxide(Ge-132) on Granuloma Formation in Rats” “Tohoku Pharmaceutical University Annual Report” 34: 263- 268 (in Japanese)
10.Kenichi Sasaki, Masaaki Ishikawa, Keiko Monma, Giichi Takayanagi 1984 “Effect of 2-Carboxyethylgermanium Sesquioxide(Ge-132) on the Acute Inflammation and CCl₄-induced Hepatic Damage in Mice” in mice “Applied Pharmacology” 27 (6): 1119-1131 (in Japanese)
11.Takayanagi, H., Ogasawara, K., Hida, S., Chiba, T., Murata, S., Sato, K., Takaoka, A., Yokochi, T., Oda, H., Tanaka, K., Nakamura, K., & Taniguchi, T., 2000, T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signaling cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-γ. Nature 408 (30): 600-605
12.Nakao Ishida and Ikuro Kimura, supervised, “Science of Organic Germanium”, “ToyoIgakusha” (in Japanese)
13.Rowan Higgs, 2010, Rheumatoid arthritis: IL-17 the multitasker – a dual role in RA pathogenesis Nature Reviews Reumatology 6,497