What is Germanium? In 1967, Dr. Asai Kazuhiko succeeded in synthesizing before the rest of the world water-soluble organic germanium, called “Asaigermanium”. Asai Germanium Research Institute has been challenging new research and its application for more than half a century (59 years).
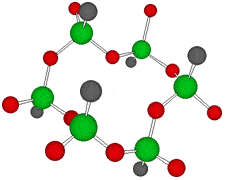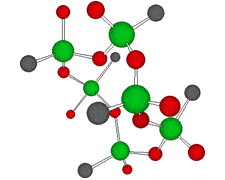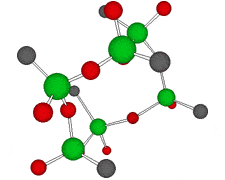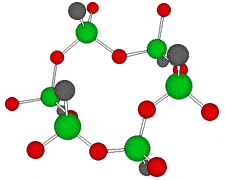
Germanium is an element symbol Ge, atomic number 32, atomic weight 72.63, an element belonging to Group 14 of the Periodic Table, classified between non-metallic “carbon” and metallic “tin, lead”, together with silicon “metalloid element” . As the name suggests, it exhibits an intermediate property between metal and nonmetal.
The germanium element lump is silvery and looks like a metal, so it is customarily called “metalicl germanium”. Actually, it is called “polycrystalline germanium”, which is gathered crystals during the process of refining germanium from extracted ore minerals, and it is hard as ceramics, but is brittle. Transistors and diodes that make use of germanium as a semiconductor have become the pioneer of electronics development, but today they have been replaced by IC semiconductors that use silicon, etc. , and industrially used in solar cells in space and infrared lenses for night vision cameras.
Asaigermanium Elements:
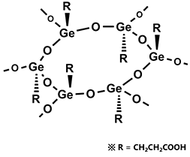
Rational formula: [(GeCH2CH2COOH)2O3]n
Chemical name: poly-trans -[(2-carboxyethyl) germasesquioxane]
Molecular weight: 339.40 (according to 2017 International Atomic Weight Table)
Solubility: 1g/100mL・water
| Standards (excerpt): | ||
| item | Standard value | Test method |
| appearance | White crystalline powder | Sensory test |
| smell | No smell | Sensory test |
| pH | 2.0-3.4 | PH measurement of 1% solution |
| Loss on drying | 0.3% or less | Japanese Pharmacopoeia (105 ℃, 4 hours) |
| Nutrition (per 100g) | |
| energy | 155kcal |
| protein | Less than 0.1g |
| Lipid | 0.2g |
| carbohydrate | 38.3g |
| Salt equivalent | 0.0g |
Stability:
*Stability in powder state: Stable tests, long-term storage tests, and accelerated tests have confirmed that it is stable to temperature, humidity, and light.
*Stability in aqueous solution: Stable tests and accelerated tests have confirmed that it is stable to temperature, humidity and light.
| Usage examples and display methods: | |
| Health foods in general (hard capsules, tablets, etc.) | (Raw material label)Organic germanium |
| Soft drink | |
| All cosmetics (cream, lotion, soap, etc.) | (Labeling Name of Cosmetic Ingredient)Repagermanium |
| Quasi-drugs (as other additives) | |
Best before date: 3 years from manufacturing date
Storage conditions: Avoid high temperature and humidity, place out of direct sunlight.
Organic germanium and inorganic germanium:
Germanium compounds are broadly divided into organic germanium compounds and inorganic germanium compounds.
Organic germanium:
Organic germanium compounds are compounds that contain Ge-C (carbon) bonds in their structure.
“Asaigermanium” (Asai-Germanium) is one of the organic germanium compounds.
Chemically, there are hundreds and thousands of types of organic germanium compounds, but different chemical structures have different physical and chemical properties and safety.
So far, Asai Germanium Research Institute have synthesized over 500 organic germanium compounds. Asaigermanium is the only organic germanium compound that has been confirmed to be safe and has various physiological activities.
Inorganic germanium:
Inorganic germanium compounds are bonded with atoms such as oxygen and sulfur, such as germanium oxides and sulfides, and have been used mainly in industrial fields. For example, germanium dioxide (GeO₂) is used as a catalyst for plastic bottle manufacturing, and germanium tetrachloride (GeCl₄) is used as an optical fiber additive.
Regarding the effects of inorganic germanium compounds (germanium oxide) on the human body, it has been reported that serious damage to the kidneys and peripheral nerves has been reported. The Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare has also issued warnings and alerts.
How to use germanium:
In the market you can find products containing Germanium such as decorations, beauty equipment, bath salts, cosmetics, health foods and more.
In some unusual places, it is also used in car battery boosters. The “Asaigermanium” is mainly used in health foods and cosmetics. Germanium used in decorative products and beauty equipment are generally inorganic germanium, and organic germanium is used in cosmetics and health foods, except for its producing area (country), manufacturing method, and quality.
In addition, most of the germanium used in the germanium bathings are thought to be organic germanium, but some of them contain a lot of toxic germanium dioxide as an impurity. Germanium bathings are characterized by a phenomenon that promotes sweating, and germanium decorations and clothing are said to promote blood circulation, but so far the mechanism seems to be unknown.
How to call Asaigermanium
Since the synthesis of Asaigermanium, there have been several names in its history.
The following names all refer to “Asaigermanium”.
① β -Bis-Carboxyethylgermanium sesquioxide
The chemical name when it was announced to the Chemical Society of Japan in 1967.
②2-carboxyethylgermanium sesquioxide
The chemical name used in the 1970s and 80s.
③Ge-132
This is the development number in Asai Germanium Research Institute company, and has been published as an abbreviation in many papers.
④poly- trans -[(2-carboxyethyl) germasesquioxane] (abbreviation: p.t-CEtGeO)
The chemical name determined by WHO in 1991.
⑤ Repagermanium
An international generic name determined by WHO in 1991. In 2002, started to use as an international label for cosmetic ingredients and as a cosmetic ingredients label.
⑥ Asaigermanium TM
Trade name for health food and cosmetic ingredients.
What is Germanium? In 1967, Dr. Asai Kazuhiko succeeded in synthesizing before the rest of the world water-soluble organic germanium, called “Asaigermanium”. Asai Germanium Research Institute has been challenging new research and its application for more than half a century (59 years).

